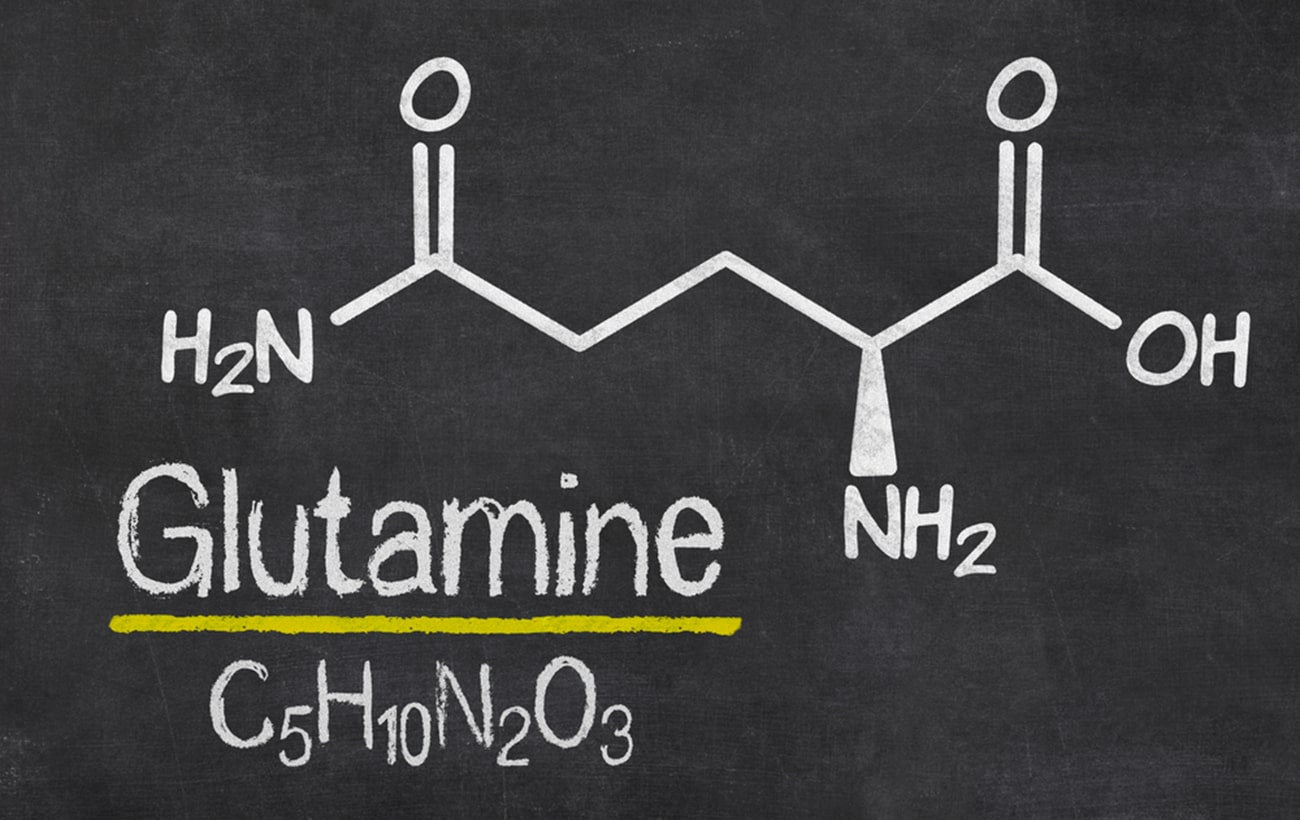
Glutamine is the most abundant amino acid in the blood and muscles. It plays an important role in protein synthesis and immune system function. It is not directly considered an essential amino acid.
An essential amino acid is an amino acid that the body cannot produce and therefore must be obtained through diet.
However, muscle and blood glutamine levels drop drastically during intense physical exertion, and while the body can synthesize some of it, depending on the physical activity performed or in cases of physical stress, it cannot produce all the glutamine necessary to meet its needs. Glutamine is therefore considered semi-essential or occasionally essential.
Glutamine is found naturally in food.
Foods rich in glutamine include meat, fish, dairy products, grains, and legumes. A healthy diet naturally provides between 5 and 10 grams of glutamine per day.
In cases of increased glutamine requirements due to sport or physical stress, supplementation is considered to involve an intake of between 5 and 10 g of additional glutamine per day.
Glutamine taken as a supplement thus prevents the body from drawing on the body's protein reserves, and therefore on the muscles, to meet its needs.
Glutamine improves digestion and reduces intestinal problems. It plays a role in the normal functioning of the intestinal wall.
Glutamine plays a role in immune protection and contributes to the body's acid-base balance.


Share:
Red berry smoothie
The BCAAs